Estimation and uncertainty quantification for extreme quantile regions
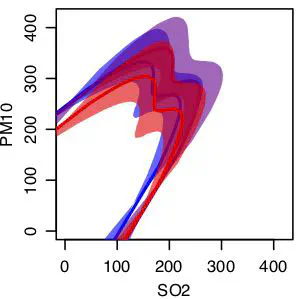 Figure 8
Figure 8+++ title = “Estimation and uncertainty quantification for extreme quantile regions” date = 2021-06-01T00:00:00
2021-03-07
draft = false
Authors. Comma separated list, e.g. ["Bob Smith", "David Jones"].
authors = [“B. Beranger”, “S.A. Padoan”, “S.A. Sisson”]
Publication type.
Legend:
0 = Uncategorized
1 = Conference paper
2 = Journal article
3 = Manuscript
4 = Report
5 = Book
6 = Book section
publication_types = [“2”]
Publication name and optional abbreviated version.
publication = “In Extremes”
publication_short = ""
Abstract and optional shortened version.
abstract = “Estimation of extreme quantile regions, spaces in which future extreme events can occur with a given low probability, even beyond the range of the observed data, is an important task in the analysis of extremes. Existing methods to estimate such regions are available, but do not provide any measures of estimation uncertainty. We develop univariate and bivariate schemes for estimating extreme quantile regions under the Bayesian paradigm that outperforms existing approaches and provides natural measures of quantile region estimate uncertainty. We examine the method’s performance in controlled simulation studies, and then explore its application to the analysis of multiple extreme pollutant occurrences in Milan, Italy.” abstract_short = ""
Is this a featured publication? (true/false)
featured = false
Projects (optional).
Associate this publication with one or more of your projects.
Simply enter your project’s folder or file name without extension.
E.g. projects = ["deep-learning"] references
content/project/deep-learning/index.md.
Otherwise, set projects = [].
projects = []
Slides (optional).
Associate this publication with Markdown slides.
Simply enter your slide deck’s filename without extension.
E.g. slides = "example-slides" references
content/slides/example-slides.md.
Otherwise, set slides = "".
slides = “example-slides”
Tags (optional).
Set tags = [] for no tags, or use the form tags = ["A Tag", "Another Tag"] for one or more tags.
tags = []
Links (optional).
url_pdf = "" url_preprint = “https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.08251.pdf" url_code = “/zip/BPS_2019.zip” url_dataset = "” url_project = "" url_slides = "" url_video = "" url_poster = "" url_source = ""
Custom links (optional).
Uncomment line below to enable. For multiple links, use the form [{...}, {...}, {...}].
url_custom = [{name = “Custom Link”, url = “http://example.org”}]
Digital Object Identifier (DOI)
doi = “10.1007/s10687-019-00364-0”
Does this page contain LaTeX math? (true/false)
math = true
Featured image
To use, add an image named featured.jpg/png to your page’s folder.
[image]
Caption (optional)
caption = “Figure 8”
Focal point (optional)
Options: Smart, Center, TopLeft, Top, TopRight, Left, Right, BottomLeft, Bottom, BottomRight
focal_point = "" +++